GPU undervolting is a technique that can help improve performance and reduce power consumption and heat output from graphics cards. With some trial and error, undervolting has the potential to yield significant benefits.
Did you know that with a little tinkering, you can get your graphics card to perform the same tasks while using less power? By reducing the core voltage supplied to the GPU, also known as undervolting, you can lower temperatures, boost clock speeds, and extend the lifespan of your graphics card – all while achieving the same level of performance or better.
Undervolting is the process of lowering the voltage supplied to the graphics processing unit (GPU) on your graphics card. By reducing voltage, you reduce power consumption and heat production. With some testing to determine stability at lower voltages, undervolting can often allow higher and more stable clock speeds. It takes some experimentation to find the optimal undervolt level for your specific GPU.
What is GPU Undervolting?
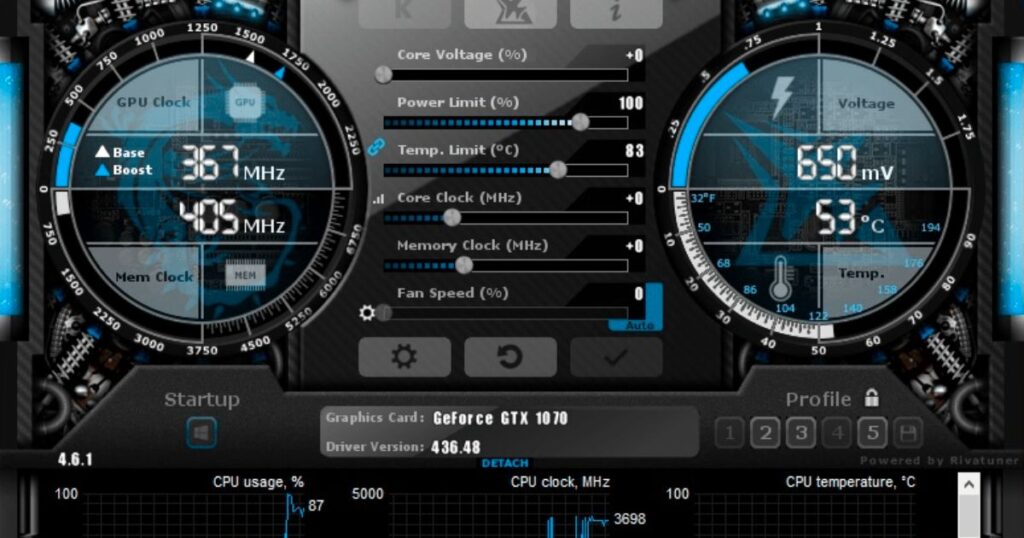
GPU undervolting involves lowering the voltage supplied to the graphics card’s processor, also known as the GPU. The GPU requires a certain minimum voltage to function properly at its default clock speeds. However, GPUs usually come with a higher default voltage from the manufacturer to ensure stability under all conditions. Sometimes resetting the graphics card to its stock settings is needed if unstable performance occurs after undervolting.
With undervolt, you reduce this voltage to the lowest stable level. This has two main benefits – it allows the GPU to run at cooler temperatures using less power, and sometimes even enables higher and more consistent clock speeds. It’s a process of carefully stepping down the voltage in small increments and testing stability each time until you find the lowest voltage that remains fully stable under load.
Benefits of Undervolting Your GPU
| Benefit | Details |
| Lower Temperatures | Reducing voltage lowers power consumption and heat output, allowing the GPU to run much cooler. |
| Increased Performance | In some cases, a successful undervolt can stabilize higher clock speeds or even achieve higher overclocks using less voltage and power. |
| Longer Component Lifespan | The reduced heat output from undervolting elongates the usable lifetime of graphics cards by protecting components from excessive heat damage over many years of use. |
| Lower Power Draw/Electricity Bills | Undervolting lowers the power draw of the entire system, saving on electricity costs over time. |
Potential Downsides of Undervolting
While undervolting can provide benefits, it is not without some risks:
The main downside is the potential for instability if the undervolt is taken too far. Pushing the voltage too low may cause software or driver crashes, visual artifacts, or BSODs under certain workloads. Thorough testing is required to find a stable undervolt point. There is also always a possibility that future hardware or driver updates could cause previously stable under volts to become unstable. However, this is rarely the case if a conservative undervolt level is used.
Another potential downside is that not all GPUs have the same overclocking/undervolting headroom. Some silicon may have very little if any voltage adjustment room left depending on the quality of the specific chip. Undervolting may provide minimal if any benefits on certain graphics cards.
How to Determine if Your GPU Can be Undervolted
There are a few key signs that indicate a GPU may benefit from undervolting:
- – If your GPU runs hot even at stock speeds and voltages. This suggests there may be headroom to lower voltage needs.
- – If your card is currently voltage or thermally throttled. Undervolting can help stabilize higher clock speeds.
- – Reviewing your GPU specifications online. High-end models from the major manufacturers often have the most adjustment headroom.
- – Checking benchmark stability at a slightly lowered voltage in software. Crashes would mean the chip may not undervolt well. Smooth benchmarking is a good start.
The silicon quality of the specific chip does matter as well. Only testing can determine the realistic undervolting potential for an individual GPU. But in general, more powerful graphics cards from the latest generations tend to benefit the most.
Choosing a GPU Overclocking Tool

- MSI Afterburner – Very full-featured with voltage/frequency controls and monitoring. Works on most GPUs.
- EVGA Precision X1 – Alternate to Afterburner, similar functionality.
- AMD Radeon WattMan – For AMD GPUs, built into the driver interface.
- Intel Graphics Command Center – For Intel integrated graphics.
These free open-source tools allow lowering the core voltage in small increments for testing stability. Monitoring software like HWInfo logs stats to analyze performance impacts.
Undervolting Process
The basic steps for undervolting are:
First, download your chosen overclocking utility like MSI Afterburner. Then locate the core voltage setting which is labeled differently between brands (i.e. mV, offset).
Next, make a small downward adjustment in voltage, such as -15mV to start. Run stress tests to check for artifacts or crashes.
If stable, repeat tests at lower increments until instability is reached. Back off slightly for daily use.
Monitor temperatures and performance during testing. The goal is to find the lowest voltage providing full stability. Results may require optimization over time.
Downloading Software
The first step is downloading appropriate monitoring and overclocking software like MSI Afterburner. This allows adjusting the core voltage setting in small increments for testing stability at lower voltages. Applications like HWInfo can log system info and help analyze performance impacts.
Finding Core Voltage Setting
Within the overclocking software, look for the setting to control core voltage which is typically labeled as “Core Voltage”, “mV”, or similar depending on the brand. This sets the voltage supplied from the power supply to the GPU core.
Testing Stability
Run stress tests like Unigine Heaven or 3DMark with monitoring software and check for artifacts, crashes, or other issues over at least 20 minutes. If stable, test in games before repeating with lower voltage. Keep testing until dialing in the lowest fully stable undervolt point.
Common Issues When Undervolting
| Potential Problem | Cause | Solution |
| Crashes in Games/Benchmarks | Voltage too low, instability reached | Raise voltage in small steps until stability is restored. |
| Artifacts/Visual Glitches | Reduce clocks if needed until thermals stabilize. | Raise the voltage a small amount for smoother operation. |
| Fan Speed Fluctuations | Voltage closer to instability point. More power draw variations. | Cooling is unable to dissipate reduced heat at high clocks. |
| Thermal Issues | Raise the voltage slightly to find a stable point. | Reduce clocks if needed until thermals stabilized. |
Undervolting Specific GPUs
Nvidia GPUs are generally very amenable to undervolting in modern architectures. Look for Pascal, Turing, and Ampere cards especially to show good results. AMD GPUs since RX 5000 series also benefit well from undervolting. With testing, even some lower-end and integrated Intel GPUs can see improvements.
Undervolting Nvidia GPUs
Nvidia GPUs are commonly very responsive to undervolting, especially newer architectures like Pascal, Turing, and Ampere. High-end cards from the GTX 10-, RTX 20-, and RTX 30- series often have significant headroom for dialing in an optimized undervolt.
Undervolting AMD GPUs
AMD GPUs since the RX 5000 lineup typically show strong undervolting potential. Models like the RX 5700 XT, RX 6700 XT, and RX 6800 perform very well when undervolted through tools like WattMan. Look for decent gains on current Ryzen APUs as well.
Undervolting Intel GPUs
While integrated Intel graphics may not overclock much, some lightweight undervolting can lower temperatures a few degrees. On CPUs with Intel Xe graphics like Iris Plus, small negative offsets sometimes provide more stable operation. Benefits are modest but possible with testing.
Potential Overclocking After a Successful Undervolt

If stability can be maintained at a lower voltage through undervolting, this sometimes creates additional headroom to apply a bit of overclocking as well. Reduced heat and power consumption allow pushing clocks slightly higher than factory settings.
Simply try increasing clock speeds like +50MHz and stress testing. If stable, performance gains can come from both undervolting efficiency and a minor overclock multiplied together. However, stability always takes priority so don’t force over-ambitious combinations.
Frequently Asked Questions About GPU Undervolting
What is the best tool for undervolting GPU?
The most popular and full-featured tool for undervolting NVIDIA and AMD GPUs is MSI Afterburner. It allows fine-grained voltage control needed for testing stability.
Does undervolting increase GPU life?
Yes, undervolting can increase the lifespan of a GPU by reducing long-term exposure to high temperatures which is a major cause of component degradation over time. Lower voltages and temps can prolong the usable life of graphics cards.
How do I Undervolt a GPU?
The basic steps are to download a tool like MSI Afterburner, locate the voltage setting, make a small voltage reduction, stress test for stability, and repeat lowering voltage in increments until instability occurs. Then back off slightly to find your optimal undervolt level.
Is it safe to Undervolt GPU?
In most cases, yes, undervolting a GPU can be safe if done properly through gradual testing and not overly aggressive undervolting. However, there is always a risk of instability or artifacts if voltage is lowered too far. It is best to only undervolt within the operating specifications of your specific graphics card model.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GPU undervolting is a technique that has the potential to provide various benefits like improved thermals, lower power consumption, and in some cases even increased performance. With some experimentation using tools like MSI Afterburner, you can evaluate your specific graphics card’s capabilities and dial in an optimized undervolt setting. While it requires taking careful steps to test stability at lowered voltages, undervolting is a simple way to potentially extend the life of your GPU and optimize its operation with very little effort. For most gaming PCs, exploring the undervolting headroom of modern Nvidia and AMD graphics cards is worth the time spent benchmarking and finding each GPU’s lowest safe voltage point.
With diligent testing and patience, GPU undervolting can unlock hidden optimizations and provide a more efficiently running graphics card. Just remember to always prioritize stability, as pushing too far can potentially cause issues. But for many systems, an undervolt tuned for each GPU delivers multiple benefits adding up to an enhanced experience from the same hardware.











