With so many different graphics cards available from manufacturers like NVIDIA and AMD, it can be difficult to know exactly which GPU is powering your system. However, being able to identify your GPU is important for a variety of reasons such as checking system specifications, seeing if your GPU supports the latest games and features, troubleshooting hardware issues, and more. In this article, we’ll go over several methods you can use to find out what graphics processing unit (GPU) you have installed on your computer.
Checking System Properties
One of the easiest ways to check your MSI Graphics Cards GPU is by looking at your system properties in Windows. This will provide basic identification information about your graphics card.
On Windows 10/11:
- Press the Windows key or click the Start menu and type “System Information”
- Click on “System Information” in the search results
- Scroll down the left panel and expand the “Components” section
- Select “Display” and look for the “Name” field, which will list your GPU model
On Windows 8/8.1:
- Right-click the Start button and select “System”
- Click on “Device Manager” in the left menu
- Expand the “Display adapters” section
- The top item listed will be your graphics card model
On Windows 7:
- Right-click the Computer icon and select “Properties”
- Click on “Device Manager” in the left panel
- Expand the “Display adapters” section
- Your GPU will be listed at the top
The model name shown should identify the make and specific graphics card that you have installed. For example, it may say “NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1060” or “AMD Radeon RX 5700”.
Checking Desktop Properties
Another quick way to check your GPU on Windows is by right-clicking on the desktop and checking the display adapter listed in the desktop properties.
To check desktop properties:
- Right-click on an empty area of your desktop
- Select “Display Settings”
- Look for the “Graphics” section and it will list your graphics card model
This method works the same across all recent versions of Windows and provides a simple way to identify your GPU without having to dive into system settings.
Checking Manufacturer Websites

Both NVIDIA and AMD maintain driver download pages where you can check your specific graphics card model. Downloading the latest drivers is also recommended to keep your GPU functioning optimally.
To check on the NVIDIA website:
- Go to www.nvidia.com/Download/Find.aspx
- Click “Auto-detect” to scan your system
- It will detect your NVIDIA GPU model
To check on the AMD website:
- Go to www.amd.com/en/support
- Select your operating system and product type as “Graphics”
- Click “Detect” and it will find your AMD graphics card
Checking manufacturer websites ensures you get the exact make and model of your graphics processor. You can also confirm you have the latest optimized drivers installed for best performance.
Using GPU-Z
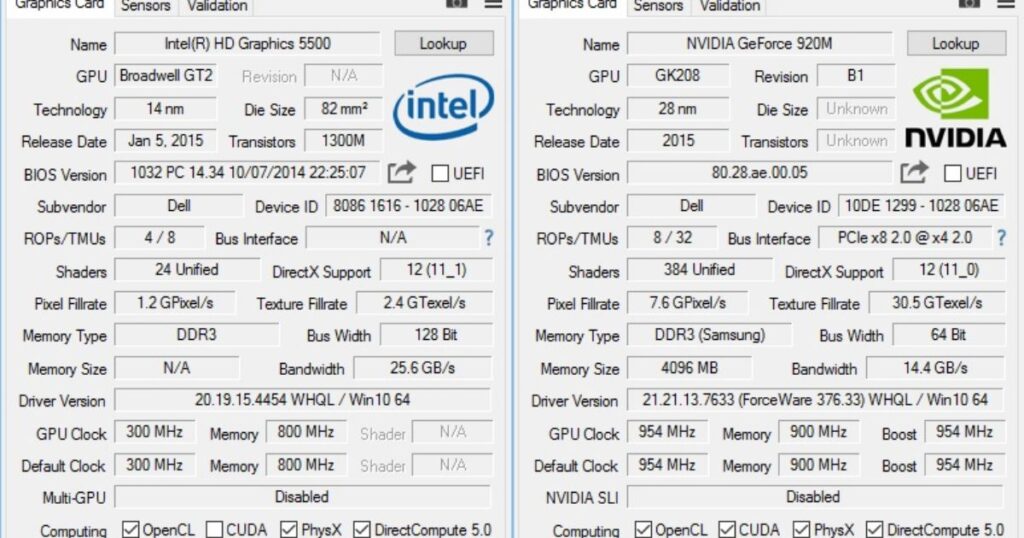
For a more detailed diagnosis of your GPU specs, the free third-party utility GPU-Z is very useful. It provides in-depth hardware information beyond just the model name.
To use GPU-Z:
- Download and install the latest version of GPU-Z from www.techpowerup.com/download/gpu-z
- Launch GPU-Z and go to the “Graphics Card” tab
- It will display the full name, core clock speeds, memory details, driver version, and more
GPU-Z gives a complete technical breakdown of your graphics processor. You can confirm specifications like VRAM amount, manufacturing process node size, BIOS version, and other identifiers. This tool is great for enthusiast users to fully analyze their GPU hardware.
Checking Physical Components
If all else fails, you can remove your PC case side panel and visually inspect the graphics card to read the model name directly off the board. However, this requires physically accessing the components inside your system.
To check the physical card:
- Power down your PC and unplug the power cable from the back
- Remove the side panel of your computer case
- Locate the graphics card (it’s typically a larger expansion card)
- Read the model name printed on the board near the display outputs
This is usually a last resort method if software identification doesn’t work. But often the make and full model will be clearly labeled. Just be mindful of proper static prevention techniques when handling PC hardware.
Finding Specific GPU Details

Once you’ve identified the basic model of your graphics card, you may want to research details like specifications, generation, performance benchmarks, or other identifying features to fully understand what GPU you have.
Checking Specification Sheets
Manufacturers provide detailed specification sheets for all of their graphics cards that outline the technical highlights. These are very useful references for looking up card details.
To find specification sheets:
- Perform an online search for your GPU model name along with “specs”
- Manufacturer websites like AMD.com and NVIDIA.com have archives of specs
- Third-party sites also maintain spec sheet databases like TechPowerUp
- Review the sheet for details like core clocks, VRAM, ports, dimensions, etc.
Spec sheets are definitive sources for confirming all the nuts and bolts components and capabilities of your particular graphics processor. Don’t rely on memory – having the official documentation is very valuable.
Determine GPU Generation
Graphics cards are often part of multi-generation families from the same company. Being able to identify which generation your model belongs to helps provide useful context.
Common GPU generations include:
- NVIDIA: GeForce 600, 700, 900, 1000, 2000, 3000, etc. series
- AMD: Radeon HD 5000, 6000, R7/R9 200, RX 400/500 series, RX 5000/6000 series
To find generation:
- Check product name for generation series number
- Research the model online or check the manufacturer’s history
- Older cards may also have physical indicators like cooler shroud designs
Understanding where a card fits in a product lineage sheds light on relative performance levels versus newer iterations for things like gaming capability or feature compatibility.
Cross-reference Reviews
Major tech sites extensively test and benchmark all major GPUs when they are new. Reading contemporary reviews of your specific model can reveal lots of valuable insights.
To find reviews:
- Search “[GPU model] review” and check the date range
- Sites like AnandTech, TechPowerUp, and Tom’s Hardware have archives
- Look at performance tests, thermal/noise ratings, overclocking headroom
- Notes on driver maturity, and common issues can be enlightening
Contemporary third-party analysis and real-world feedback are very informative compared to just specs alone. It paints a full performance and user experience picture.
Checking Packaging/Box Arts

If you happen to still have the original retail packaging for your graphics card, it can offer some definitive identification clues that spec sheets may lack.
What to look for on boxes:
- Model name prominently displayed
- Chipmaker logo like AMD or NVIDIA
- Board partner names like Asus, Gigabyte, MSI, etc.
- Sometimes lists key specs or feature highlights
- May have barcode/product number to further research
Retail boxes are often more vivid than just the hardware itself. Photographs of box art are also commonly found online which can be useful vintage identifiers.
Decoding Specific GPU Details
Now that you’ve gathered details on your graphics card, there may still be finer points that require deciphering manufacturer-specific nomenclature or component identifiers on certain models.
Understanding GPU Chip Codenames
Both AMD and NVIDIA utilize internal codenames for their graphics processors beyond just the consumer product names. These provide extra insight for researchers.
Common GPU chip codenames:
- NVIDIA: Kepler, Maxwell, Pascal, Turing, Ampere, Lovelace
- AMD: Tahiti, Hawaii, Fiji, Polaris, Vega, Navi
To find codenames:
- Search “[GPU model] codename”
- Spec sheets may specify internal designations
- Hardware database sites decode them
- Enthusiast forums are knowledgable
Chip architecture codenames connect generations and provide low-level technical context beyond just marketing names.
Decoding GPU Variants
Certain popular gaming-focused GPU models often have multiple similar variants with minor differing specs sold under the same product family name.
Common variants include:
- Core config – Number of SMs/ALUs enabled
- Core clock speeds – Different boost bin levels
- Memory type/capacity – GDDR5 vs GDDR6, 2/4/8GB
- Cooler design – Blower vs dual/triple fan
To identify variants:
- Check specs against options for the specific product line
- Look for unique model identifiers like “Super” or “Ti” in the name
- Search online for the full model number/name
- Compare component configs to release notes from manufacturers
- Enthusiast databases sometimes list different SKUs
Spending time cross-checking the subtle variations can give a complete picture of where a particular card fits in the family.
Understanding GPU Generations
As graphics cards progress through architectural generations from AMD and NVIDIA, certain naming conventions become standardized indicators of when a model was released.
Common generational markers include:
- Three-digit naming scheme (e.g. GTX 680) indicates Kepler/GCN 1
- Four-digit prefix with an “X” (GTX 1060) indicates Maxwell/GCN 3
- Two-digit prefix starting in “2” (RTX 2060) indicates Turing/GFX10
- Three-digit prefix starting in “3” (RTX 3070) indicates Ampere/RDNA
To correlate generation:
- Research the GPU architecture codename
- Check release year against company roadmaps
- Overlapping numbering schemes can exist
- Enthusiast sites correlate model names to ages
Putting the graphical processor in its proper period based on naming patterns provides historical context for the technology.
Identifying Memory Configurations
RAM specifications are another way variants and architectures differ that may require deeper research.
Key memory identifiers include:
- Interface type – GDDR5, GDDR6, HBM, etc.
- Memory bus width – 128-bit, 256-bit, etc.
- Total VRAM amount – 2GB, 8GB, 16GB
- Memory clock speed
- Memory bandwidth
To decode memory:
- Refer to spec sheets for your exact GPU
- GPU-Z reads the current configuration
- Search ‘[model] VRAM’ for variants
- Memory is often a limiting factor for newer games
Confirming the recollections RAM helps gauge performance potential years after purchase.
FAQ’s
What GPU drivers do I have?
- Check the Device Manager in Windows or use GPU-Z to see the currently installed graphics driver version.
How do I check my graphics card online?
- Visit the manufacturer’s website (AMD or Nvidia) and use their auto-detection tool to scan your system and identify the GPU model.
How do I know which Nvidia GPU I have?
- Go to nvidia.com/driver and select “Auto-detect” which will scan your system and show you the specific Nvidia GPU model.
How do I know what my GPU is?
- Check your system properties in Windows, look at the desktop properties display adapter, or open the computer case and look at the graphics card directly to see the model name printed on it.
Conclusion
Being able to correctly identify the graphics processing unit inside your system is an important first step for several tasks like keeping your drivers updated, benchmarking performance, troubleshooting issues, and learning specifics about your hardware. This article provided many methods for determining your GPU model through Windows and manufacturer utilities, reference documentation, and direct inspection. Arming yourself with knowledge of the fundamental details, variances, and generational context around your graphics card can enhance your PC experience.
With the PC gaming and graphics processing industries constantly evolving new architectures and products each year, keeping track of older hardware specifications can become challenging over time. However, taking the time to fully decode your GPU – from the basic model name down to intrinsic component configurations – ensures you understand its full capabilities. You’ll be in a better position to continue maximizing its performance as new software demands evolve. Identifying your graphics card is a valuable exercise for any enthusiast wanting to get the most out of their system.